ALE CALCULATION TOOL USING LAST CALENDAR YEAR EMPLOYEES AND HOURS FOR WHICH PAY IS RECEIVED
Next steps: Add ALL 12 months Total FT and FTE count and divide by 12 to determine average monthly FT and FTE Count for entire year. Round the final number down to a whole number to determine your ALE status.
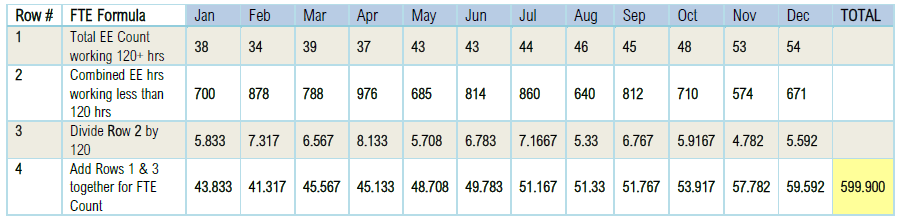
599.900/ 12 = 49.992 Rounded down to 49 FT and FTEs
Results Analysis: The example above determines the sample employer is not an Applicable Large Employer (ALE).
REMEMBER THAT Certain employer aggregation rules apply in determining whether an employer is an ALE subject to the employer information reporting provisions. Under those rules, all employers treated as a single employer under Internal Revenue Code section 414(b), (c), (m), or (o) are treated as one employer for purposes of FTE calculation and determining ALE status. The employers that comprise the Aggregated ALE Group are each referred to as ALE Members. Source: https://www.irs.gov/affordable-care-act/employers/information-reporting-by-applicable-large-employers
FORMULA TO USE
The ALE formula is based on the employer’s size for a calendar year (12 months). Using the formula below, calculate the previous calendar year and that determines the Employer size and ACA obligations for the next calendar year (ie calculate the FT and FTE count Jan-Dec 2022 to determine Employer size for 2023). If an employer has 50 or more Full-Time (FT) and Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) employees in the previous calendar year, the employer is considered an ALE for ACA purposes and additional obligations apply.
For purposes of determining if the employer is an ALE, the formula requires the following steps:
1. Determine the total number of FT employees (including any seasonal employees) for each calendar month in the preceding calendar year. This is based on hours for which pay is received. Anyone with 120+ hours in a month is considered FT and counted as 1 for the month. But see note regarding seasonal workers below.
2. Determine the total number of FTE employees (including any seasonal employees) for each calendar month in the preceding calendar year. Again, this is based on hours. For any employees with less than 120 hours in a month, add their hours together and divide this number by 120 to determine the number of FTE employees for the month.
3. Add the number of FT employees and FTE employees determined in Steps 1 and 2 above for each month of the calendar year.
4. Divide the total FT employees and FTE employees determined in Step 3 by 12. Round down any fractional number to the nearest whole number. This is the average FT and FTE employee count.
If the average FT and FTE count is 50 or more, the employer is an Applicable Large Employer (“ALE”) and must comply with offering coverage and additional reporting obligations or face ACA penalties.
Example: During each month of 2021, an employer has 35 full-time employees, each of whom has 35 hours of service per month, and 40 part-time employees, each of whom has 90 hours of service per month. In this example, each of the 35 employees who has 135 hours of service per month count as one full-time employee for each month. To determine the average number of full-time equivalent employees for each month, take the total hours of service of the part-time employees (but not more than 120 hours of service per employee) and divide by 120. The result is that the employer has 30 full-time equivalent employees each month (40 × 90 ÷ 120 = 30). By adding the two categories of employees together, the employer would have 65 full-time and full-time equivalent employees. Therefore, the employer is an applicable large employer for 2022.
Note if an organization employs Seasonal Workersi(1) and the FT and FTE count is 50 or more due to the seasonal workers, the employer is not considered an ALE. Specifically, the rule states: If an employer’s FT and FTE employee count exceeds 50 for 120 days or less in the last calendar year, and all of the employees in excess of 50 during that time were seasonal workers, that employer is not an ALE. Source: https://www.irs.gov/affordable-care-act/employers/determining-if-an-employer-is-an-applicable-large-employer
REFERENCES
Determining if an Employer is an Applicable Large Employer | Internal Revenue Service (irs.gov)
IRS Employer Shared Responsibilities FAQs: https://www.irs.gov/affordable-care-act/employers/questions-and-answers-on-employer-shared-responsibility-provisions-under-the-affordable-care-act#Employers
Legal Disclaimer: The materials and information contained herein are intended only to provide general information and in no way constitute legal advice. While these resources are provided in consultation with federal and state statutes, please be aware that additional applicable regulations, laws, and legal considerations may exist. Therefore, if you have specific questions or concerns, please consult legal counsel. Please also be aware that the information provided is current as of this date and the information contained herein is subject to change.